Printed
Circuit Board – An Overview
Printed
circuit board (PCB) is a highly reliable and durable physical circuit design
that has become an essential component of any electronic device. Printed
circuit boards are made of a very thin substrate board embedded with electronic
components interconnected using thin-layer of copper interconnecting traces.
The board substrate is usually made of fiberglass composite epoxy substrate or
other laminate materials. The circuit will contain both active and passive components.
With more advanced and smaller component availability it is possible to
accommodate a very large and complex circuit in a small PCB design.
PCBs are of three types. Single side, Double side, and Multi-layered boards. Single-sided boards have the components on one side of the substrate. Double side have components on both sides. In a multi-layered board, multiple layers of printed circuits are separated by insulation layers. In double-sided and multilayer PCBs components are interconnected by drilling holes at appropriate points and plating them with conducting materials.
Major Advantages of PCB
1.Smaller
and Thinner in size.
2.Highly customizable in design and application.
3.Durable, Reliable and long life.
4.Easy to debug and easy to repair.
5.Low cost.
Various Steps in PCB Design and Manufacturing
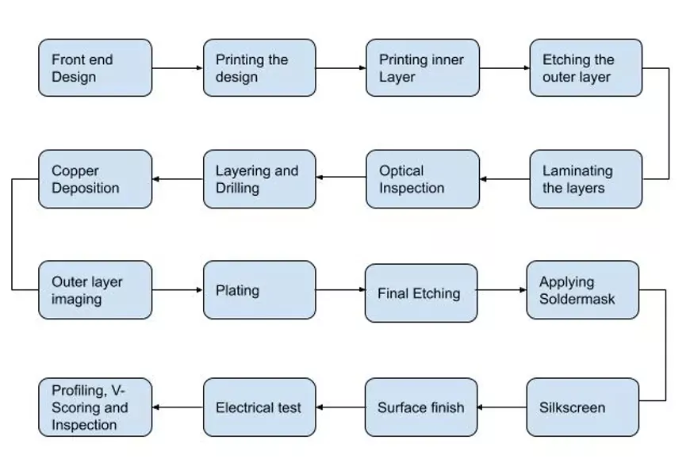
Step 1: Requirement analysis and Component selection
Next step is to run Design for Manufacture (DFM) check before circuit boards fabrication starts. This is to avoid any discrepancies in design. After this, a photo film is made to image the PCB using a laser printer/plotter. Different layers of the PCB photo film are aligned by punching precise registration holes in each sheet of film. The film is created to help in creating a figure of copper path.
Step 17: Final inspection and packing
PCB design process is a requirement driven and highly customizable process enables us to produce specific circuit function whether complex or simple. Cleanliness and precision are the most important precautions to be followed in PCB design and manufacturing
